
For example, I chose the default domain name-and the hostname I entered is skulltech. The address you will get is hostname.domain. You can also choose a domain name from a list there. When you get to the dashboard, go to Dynamic DNS → Hostnames and add a hostname of your choice from there. There are many DDNS providers, I’m going to use No-IP which is one of them.
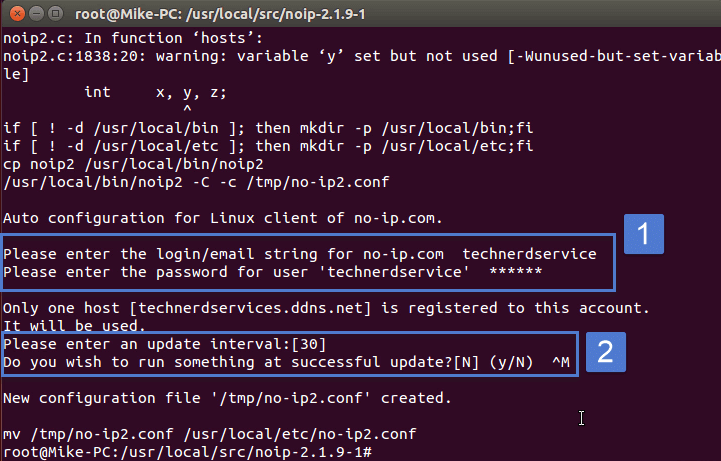
#No ip duc linux command update
DDNS servers update the DNS record of your machine continuously, so that even for dynamic IP machines the domain name resolves to the correct IP, always. But the problem of your IP being dynamic still remains. Similarly you can get a domain name for your machine and put that domain name in the place of HOST IP address in your payload. When you try to connect to a domain name, for example opening on a browser, the request first goes to a DNS server, which resolves the domain name into an IP, and then the browser gets the Google homepage from that IP. We all know what DNS or Domain Naming System is, it’s the system which binds an IP to a domain name. But as dynamic IP keeps changing from time to time, you won’t be able to use a payload for a long time because after some time the IP stored inside it won’t point to your machine anymore. When it gets executed, it connects back to the host machine by the reference of that host IP. Reverse connection payloads, such as android/meterpreter/reverse_tcp, store the host IP address, i.e. Having a dynamic IP address is a hindrance to hacking using reverse connection payloads. You can check what’s your public IP by googling “What is my IP”, Google will tell you. Most of the ISPs provide dynamic public IP, that means it changes from time to time, contrary to the static one, which remains fixed. For connecting to the Internet they use the router’s public IP. Each of them has a locally unique private IP address, not globally. For example, if two or more machines are connected through a router-maybe through Wi-Fi-to the internet, then the machines are in a local network, as well as both of them are connected to the Internet. Public IP is the IP that’s visible to machines outside your local network. But I’m getting ahead of myself, so let me start by explaining what is public IP and what are some problems you can encounter if you have a dynamic one. I’m going to discuss in this post how you can overcome that using Dynamic DNS or DDNS. That poses some problems if you want to use that connection to host a website, or maybe for hackers like us, to hack using reverse connection payloads. Many of us have an internet connection with a dynamic public IP.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
